
|
|
VARIABLE FACTOR OF PRODUCTION: An input whose quantity can be changed in the time period under consideration. This usually goes by the shorter term fixed input and should be immediately compared and contrasted with fixed factor of production, which goes by the shorter term fixed input. The most common example of a variable factor of production is labor. A variable factor of production provides the extra inputs that a firm needs to expand short-run production. In contrast, a fixed factor of production, like capital, provides the capacity constraint in production. As larger quantities of a variable factor of production, like labor, are added to a fixed factor of production like capital, the variable factor of production becomes less productive.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           MARGINAL REVENUE CURVE, PERFECT COMPETITION: A curve that graphically represents the relation between the marginal revenue received by a perfectly competitive firm for selling its output and the quantity of output sold. Because a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker and faces a horizontal demand curve, its marginal revenue curve is also horizontal and coincides with its average revenue (and demand) curve. A perfectly competitive firm maximizes profit by producing the quantity of output found at the intersection of the marginal revenue curve and marginal cost curve. Perfect competition is a market structure with a large number of small firms, each selling identical goods. Perfectly competitive firms have perfect knowledge and perfect mobility into and out of the market. These conditions mean perfectly competitive firms are price takers, they have no market control and receive the going market price for all output sold.The marginal revenue curve reflects the degree of market control held by a firm. For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal revenue curve is a horizontal, or perfectly elastic, line. For a monopoly, oligopoly, or monopolistically competitive firm, the marginal revenue curve is negatively sloped and lies below the average revenue (demand) curve. Marginal Revenue Curve,
Perfect Competition | 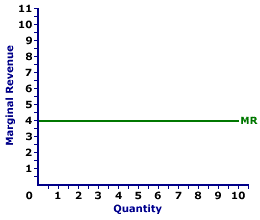 |
Marginal revenue is commonly represented by a marginal revenue curve, such as the one labeled MR and displayed in the exhibit to the right. This particular marginal revenue curve is that for zucchini sales by Phil the zucchini grower, a presumed perfectly competitive firm. The vertical axis measures marginal revenue and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of output (pounds of zucchinis). Although quantity on this particular graph stops at 10 pounds of zucchinis, the nature of perfect competition indicates it could easily go higher. This curve indicates that if Phil sells the first pound of zucchinis (an increase in production from 0 to 1), then his extra revenue is $4. However, if he sells his tenth pound (an increase in production from 9 to 10), then he also receives $4 of extra revenue. Should he sell his hundredth pound (an increase in production from 99 to 100), then he moves well beyond the graph, but his marginal revenue remains at $4. Because Phil is a perfectly competitive firm, his marginal revenue curve is also his demand curve and his average revenue curve. All three curves coincide for perfect competition.

Recommended Citation:MARGINAL REVENUE CURVE, PERFECT COMPETITION, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: April 28, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | | | |
Related Websites (Will Open in New Window)... | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
|
Approximately three-fourths of the U.S. paper currency in circular contains traces of cocaine.
|

|
|
"The roots of education are bitter, but the fruit is sweet." -- Aristotle
|

|
QR
Quantitative Restriction
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


